In the past few decades, the world of manufacturing has changed dramatically. Gone are the days when factories were filled with workers assembling products by hand. Today, robots are becoming a common sight in U.S. manufacturing plants. While they offer speed, precision, and cost savings, their growing use raises one important question—what is the impact of robotics on American manufacturing jobs?
This article dives deep into how robotics is changing the job market in the U.S., what industries are most affected, and whether automation is creating or destroying opportunities for American workers.
Table of Contents
The Rise of Robots in American Factories
Robotics has been used in U.S. manufacturing since the 1960s, but its use has grown rapidly in the last 10–15 years. According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), the U.S. now ranks among the top five countries in robot installations. Robots are widely used in industries like automotive, electronics, metal, and even food processing.
These machines can do tasks such as welding, painting, packaging, assembling, and even quality checks. They work 24/7, don’t need breaks, and don’t ask for wages. For companies, this means higher productivity and lower costs.
But for human workers, the story is more complex.
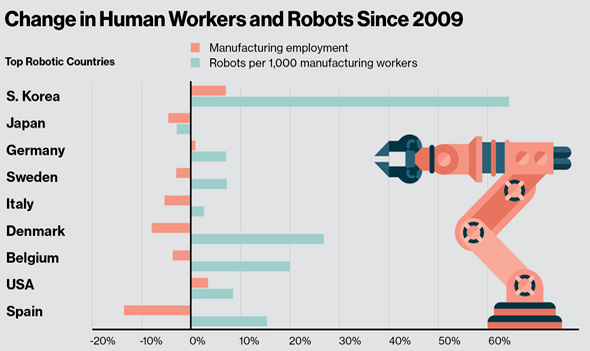
Job Losses or Job Shifts?
One of the biggest fears about robotics is job loss. Studies have shown that automation can replace low-skill, repetitive tasks, especially in sectors like car manufacturing or electronics assembly. In these areas, robots have replaced thousands of jobs once held by humans.
However, the full picture is more balanced.
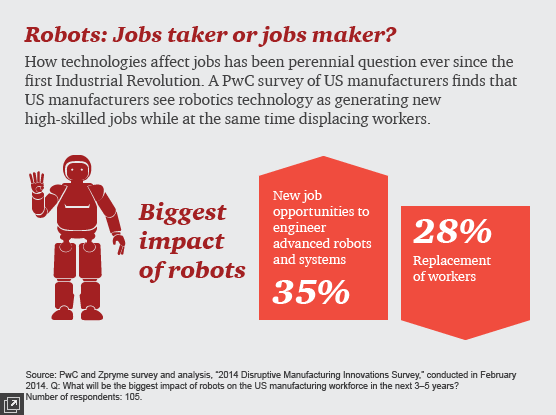
Many experts argue that while some jobs are lost, new ones are created. Robotics often leads to changes in job types, rather than total job loss. For example, workers may no longer assemble products but are instead needed to operate, maintain, and program the robots. These new roles usually require more training and pay better wages.
A 2020 report by the Brookings Institution found that jobs in manufacturing are not disappearing—they are evolving. Workers with skills in automation, robotics maintenance, and data analysis are now in high demand.
Which Workers Are Most Affected?
The impact of robotics on jobs depends on the skill level and the type of work. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Low-skill, routine jobs: These are the most at risk. Tasks that are simple, repetitive, and predictable can easily be done by robots. Workers on assembly lines are seeing fewer openings as machines take over these roles.
- Mid-skill jobs: Jobs involving supervision or decision-making are less affected. These may include quality control inspectors or team leaders.
- High-skill jobs: In demand. Robotics engineers, software programmers, and equipment technicians are seeing more job opportunities than ever before.
This shift means that workers who can adapt and learn new skills have a better chance of staying employed in the industry.
The Human Side of the Automation Story
It’s easy to focus only on numbers and trends, but the real impact is felt by people. Many workers have spent their entire careers in manufacturing, and sudden job losses due to robotics can lead to emotional and financial stress.
In towns where factories are a major employer, automation can affect entire communities. Local businesses, schools, and services all suffer when large numbers of people are laid off.
That’s why training and education are critical. Without support programs, workers may struggle to find new roles in the changing job market.
Government and Industry Response
Recognizing the challenges, both government and private companies have started investing in training programs. Many states now offer retraining options through community colleges, vocational schools, and online platforms. Some companies also offer on-the-job training to help workers transition to technical roles involving robotics.
For example, a factory worker whose job is replaced by a robot might be offered free training to become a robot technician or machine operator. These programs can help reduce the negative impact of automation.
The U.S. government has also introduced policies encouraging advanced manufacturing and investing in research and development of smart factories.
Are Robots Helping the Economy?
Despite fears, robotics can have a positive effect on the U.S. economy. Automation boosts productivity and allows companies to stay competitive in a global market. Without robots, many U.S. firms might move operations to countries with cheaper labor, resulting in even more job losses.
In fact, automation can bring back some manufacturing work from overseas. This is called “reshoring.” When factories are automated, they can produce goods in the U.S. at lower costs, making it profitable to keep production at home.
Additionally, robotics helps small and medium-sized manufacturers to grow. Affordable automation tools allow smaller firms to increase output and hire more skilled staff.
What the Future Looks Like
The future of robotics in U.S. manufacturing is clear—it will continue to grow. New technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, and smart sensors are making robots more advanced and flexible.
By 2030, experts predict that most manufacturing facilities will be “smart factories,” where humans and robots work side by side. Jobs won’t disappear, but they will be very different from what we see today.
To succeed in this new world, workers must stay updated with new skills. Lifelong learning will become a part of every worker’s journey.
Final Thoughts
Robotics is transforming U.S. manufacturing in a big way. While it may reduce some types of jobs, it also creates new opportunities that are more skilled and better paid. The key to surviving and thriving in this changing landscape is adaptability.
With the right training, support, and policies, the rise of robotics doesn’t have to be a threat—it can be a chance for American workers and industries to grow stronger than ever.
Read More :-Top 10 Tech Hubs in the USA Outside Silicon Valley






