CRISPR and cultivated meat are reshaping the future of food and farming. Together, they form a powerful duo in the world of climate-smart biotech. These technologies offer a path to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, cut down land and water use, and make the global food system more sustainable. As the planet faces growing pressure from climate change and a rising population, science-based solutions like these are no longer optional—they’re necessary.
What is CRISPR?
CRISPR stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats. It’s a gene-editing tool that lets scientists make precise changes to DNA. Originally discovered in bacteria, CRISPR allows researchers to target specific genes and turn them on or off, remove them, or replace them entirely.
It’s fast, cheap, and highly accurate, making it one of the most important biotech advances in recent years. CRISPR is already being used to improve crops, treat diseases, and enhance food production. In the context of cultivated meat, it can make meat production more efficient, nutritious, and safe.
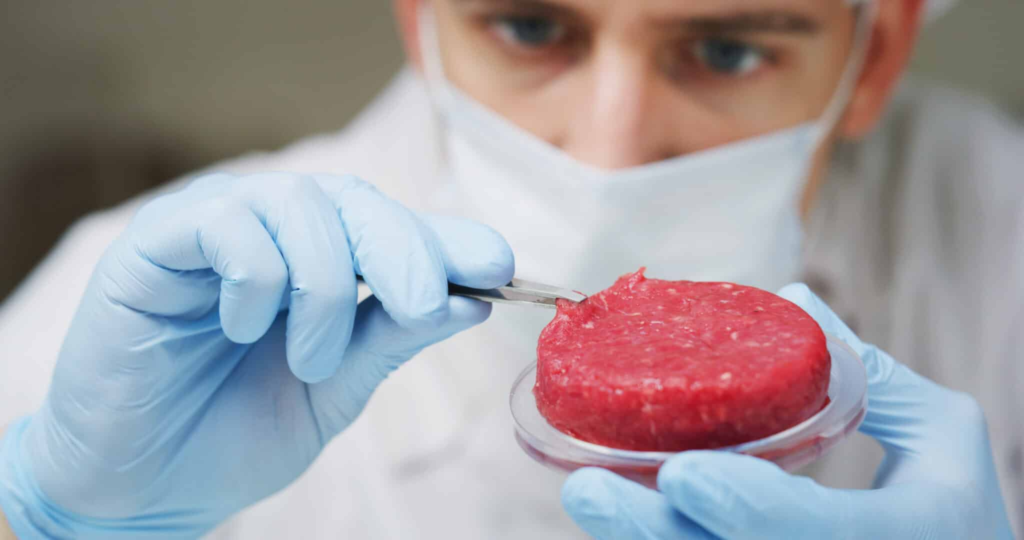
What is Cultivated Meat?
Cultivated meat is real meat grown from animal cells in a lab, without needing to raise or slaughter animals. The process starts by taking a small sample of cells from an animal. These cells are placed in a controlled environment and given nutrients to grow and multiply into muscle tissue—the same type of tissue we eat as meat.
This meat is not artificial or plant-based. It’s biologically the same as meat from a farm animal, but produced in a much cleaner and more sustainable way. It uses far less land, water, and energy and avoids many of the environmental downsides of traditional livestock farming.
How CRISPR Improves Cultivated Meat
CRISPR technology plays a key role in making cultivated meat more viable and scalable. Here are a few ways it contributes:
Faster Cell Growth
CRISPR can help optimize the cells used in cultivated meat, allowing them to grow faster and more efficiently. This reduces the time and resources needed to produce meat at scale.
Improved Nutrition
Scientists can use CRISPR to modify the nutritional content of cultivated meat. For example, adding more Omega-3 fatty acids or reducing unhealthy fats to make the meat healthier.
Disease Prevention
By editing out genes that may carry animal diseases, CRISPR can make cultivated meat safer. It reduces the risk of contamination that is common in factory farms.
Enhanced Taste and Texture
CRISPR allows researchers to fine-tune the characteristics of meat, such as texture, flavor, and color. This makes cultivated meat more appealing to consumers and helps it match traditional meat more closely.
Climate Benefits of CRISPR and Cultivated Meat
One of the biggest reasons why CRISPR and cultivated meat are gaining attention is their potential to fight climate change. Animal agriculture is responsible for a significant share of global greenhouse gas emissions—around 14.5 percent. Cultivated meat offers a cleaner alternative.
Reduced Emissions
Because cultivated meat doesn’t require livestock, it avoids the methane emissions from cows and other animals. Some studies suggest it could cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90 percent compared to beef.
Lower Land and Water Use
Traditional meat production needs large areas of land for animals to graze and crops to feed them. Cultivated meat requires a fraction of the land and significantly less water.
Less Deforestation
With less need to clear forests for pasture or feed crops, cultivated meat helps preserve biodiversity and prevent habitat loss.
No Need for Antibiotics
Livestock farming often uses antibiotics, which can lead to drug-resistant bacteria. Cultivated meat avoids this risk entirely.
CRISPR and Cultivated Meat in Climate-Smart Biotech
Climate-smart biotech refers to technologies that reduce the environmental impact of food production while improving its resilience. CRISPR and cultivated meat are ideal examples. They align with three key goals of climate-smart agriculture:
- Reduce emissions
- Improve efficiency and yield
- Support adaptation to climate challenges
In addition to cultivated meat, climate-smart biotech includes innovations like drought-resistant crops, vertical farming, and precision fermentation. Together, these technologies are creating a more sustainable and secure food system.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the promise of CRISPR and cultivated meat, several challenges still need to be addressed.
Cost
Producing cultivated meat is still more expensive than traditional meat. While costs have come down, mass-market affordability is still a few years away.
Regulation
Different countries have different rules when it comes to gene editing and lab-grown food. Some, like the U.S. and Singapore, are more welcoming, while others are more cautious.
Consumer Acceptance
Some people are hesitant to try meat grown in a lab or modified with gene editing. Public education and transparency will be key to building trust.
Ethical Questions
While many see cultivated meat as a more ethical option than slaughtering animals, some critics worry about the long-term impacts of gene editing and lab-based food.

Looking Ahead: The Future of Food
The next decade will be critical in shaping the role of CRISPR and cultivated meat in our food system. We are likely to see:
- Lower production costs, making lab-grown meat competitive with conventional options
- More regulatory approvals around the world
- Wider availability in supermarkets and restaurants
- New companies combining CRISPR, cultivated meat, and plant-based technology to create hybrid foods
Eventually, we may see a complete shift in how meat is made—moving from farms to food labs powered by sustainable biotech.
Leading Innovators
Several companies are leading the way in CRISPR and cultivated meat:
- Upside Foods is one of the first to gain U.S. approval for cultivated chicken
- GOOD Meat is already selling lab-grown chicken in Singapore
- Mosa Meat, based in the Netherlands, helped create the first lab-grown burger
- TurtleTree Labs is working on cell-based dairy and infant nutrition
- Tropic Biosciences uses CRISPR to improve crops like bananas and coffee
These companies are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in climate-smart food technology.
Conclusion
CRISPR and cultivated meat are not just futuristic concepts—they’re real solutions to some of today’s biggest problems. They offer a way to feed a growing population without exhausting our planet’s resources. By reducing emissions, saving land and water, and offering safer, more ethical food, these technologies are helping to build a climate-smart future.
If we want to meet the challenges of climate change, reduce environmental harm, and still enjoy the foods we love, CRISPR and cultivated meat may be our best bet.
Do Follow USA Glory On Instagram
Read Next – AI Literacy in Schools: Federal Push Transforms Education






