Subscription-based business models are changing how people buy, use, and stay loyal to products and services. From Netflix to meal kits, software to streaming, subscriptions are now a major part of the economy. As more companies switch from one-time purchases to recurring billing, this shift is creating new opportunities—and challenges—for businesses and consumers alike.
What Is a Subscription-Based Model?
A subscription-based business model is one where customers pay a recurring fee to access a product or service. This could be monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Instead of owning something outright, users pay to use it over time.
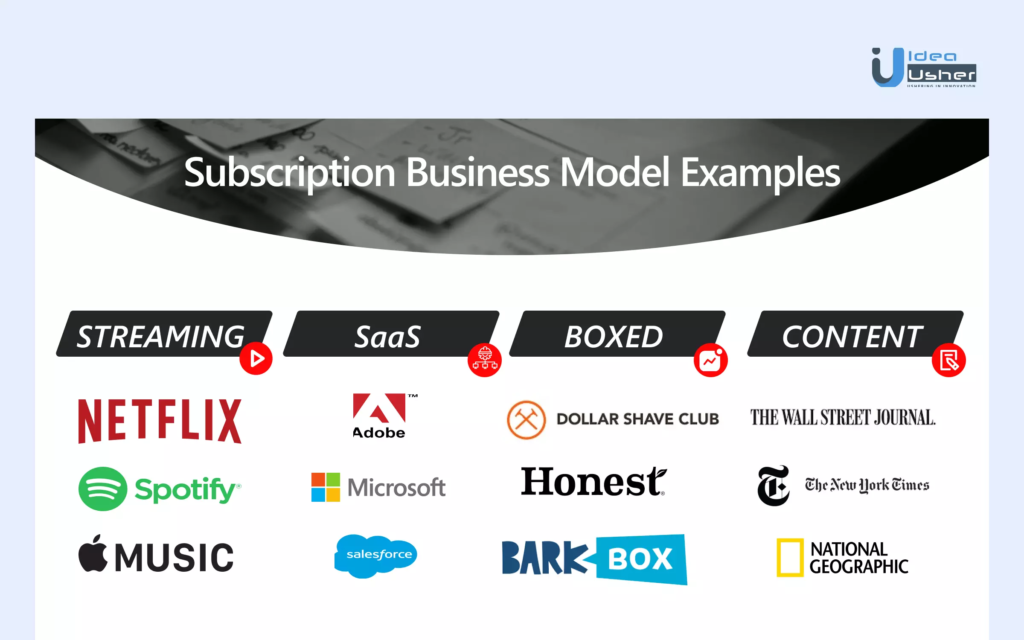
Popular examples include Netflix, Spotify, Amazon Prime, Microsoft 365, and even subscription boxes like Dollar Shave Club or Blue Apron.
Why Are Businesses Choosing Subscriptions?
There are several reasons why businesses are turning to subscriptions:
1. Predictable Revenue
Subscriptions provide stable and predictable income. This allows companies to better plan their finances and scale operations. It also reduces the uncertainty that comes with one-time sales.
2. Customer Loyalty
With recurring payments, companies stay connected to their customers longer. That ongoing relationship builds brand loyalty and increases customer lifetime value.
3. Easier Upselling and Personalization
Subscription models allow businesses to collect data over time. This helps them understand user habits and tailor services or offers, which can increase spending and satisfaction.
A detailed guide on how businesses are adopting these models is available on Harvard Business Review.
Key Industries Adopting Subscription Models
Subscription models are no longer limited to media or magazines. Today, they are being used across multiple industries:
1. Technology and Software
Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms like Adobe Creative Cloud, Dropbox, and Zoom rely heavily on subscriptions. They offer tiered pricing and regular updates, which keep users engaged and paying.
2. Entertainment and Media
Netflix, Disney+, Hulu, and Spotify are perfect examples of subscription-based media platforms. Users pay a monthly fee for unlimited access to movies, music, and shows.
3. E-commerce and Retail
Companies like Dollar Shave Club, Stitch Fix, and Amazon Subscribe & Save offer products on a recurring delivery basis. These create convenience and ensure steady product sales.
4. Food and Meal Delivery
HelloFresh and Blue Apron are top players in the subscription meal kit market. They send fresh ingredients to subscribers weekly, making cooking easier for busy individuals.
5. Education and E-learning
Platforms such as Coursera Plus and MasterClass use subscriptions to give learners access to courses and expert content. These services are affordable alternatives to traditional education.
Benefits to Consumers
Subscription services offer more than just convenience. They also help users get more value over time.
- Lower upfront cost: Instead of paying a large sum all at once, users can spread out costs.
- Ease of access: Services are often available anytime and from anywhere.
- Customization: Many services personalize recommendations based on usage.
- Automatic delivery: Consumers don’t have to worry about running out of essential items.
Challenges of Subscription Models
While there are many benefits, subscription-based models also come with some drawbacks.
1. Subscription Fatigue
Consumers are now juggling multiple subscriptions—streaming, fitness, groceries, software, and more. Over time, these can become too expensive or hard to manage. Many are canceling unused services to save money.
2. Churn Rate
Businesses must work hard to keep subscribers engaged. If users don’t find continuous value, they will cancel. Retaining customers is now as important as acquiring them.
3. Complex Pricing Strategies
Finding the right pricing structure is a challenge. Companies must balance value with profit. Too high, and customers leave. Too low, and businesses lose revenue.
4. Payment and Security Concerns
Recurring payments mean sensitive financial data is stored online. Businesses must invest in secure payment systems to protect user information and build trust.
Future of Subscription-Based Business Models
The subscription economy is expected to keep growing. According to a report from Statista, the global subscription economy could reach over $1.5 trillion by 2025.
Companies are now exploring hybrid models. For example, car companies like Porsche and Volvo offer car subscriptions instead of ownership. Fitness companies are offering both in-person classes and virtual memberships.
AI and machine learning are also playing a role. They are helping businesses personalize user experiences and predict when a subscriber might cancel.
Tips for Businesses Entering the Subscription Market
For companies considering a move to subscription models, here are a few tips:
- Start with a free trial or freemium option to attract users
- Use customer feedback to improve services continuously
- Offer flexible pricing tiers to appeal to a wider audience
- Invest in customer service to resolve issues quickly
- Track metrics like churn rate, lifetime value, and conversion rates
Tools like Zuora and Chargebee help manage billing, analytics, and customer data effectively.
Conclusion
Subscription-based business models are more than just a trend—they’re becoming the future of commerce. From tech and entertainment to education and groceries, subscriptions are making business smoother for companies and more convenient for consumers.
But success in the subscription economy requires more than just a recurring bill. It demands ongoing value, smart marketing, and a deep understanding of customer needs. Companies that can master this balance are likely to thrive in the years to come.
Explore more resources on subscription growth and business innovation here.
Also Read – Top Stock Market Trends You Must Know Before Investing






